This site has moved, click here to go to the new site
The following is a complete listing of orientation algorithms for the SOAP method. For a full explaination of this method, see here.
I recommend learning them in the order in which they are presented below. For all cases, the first alg listed is the one which I think is the quickest to do. For cases where this is not a 2-gen algorithm, I have also provided at 2-gen alg for the case. Using 2-gen algorithms allows you to easily predict the PBL, which is explained in the above-mentioned page. 2-gen algorithms will have an [s] after them if they cause a permutation swap on the bottom layer. "Pure" algorithms which don't affect permutation have a [p] after them.
Ortega Subset
The first 7 cases are simply the orientation algorithms from the Ortega method. You use these when you solve a complete face on the bottom layer. I won't be printing these here, because I'm assuming that you already know Ortega before starting with SOAP.
SS Subset
The following 16 algorithms are also used in the SS method. These are used when a single corner in the bottom layer is unoriented. This unoriented corner should always be held in the Bottom-Right-Front position.
Bottom →
Top ↓ |
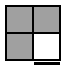 |
Bottom →
Top ↓ |
 |
 |
FRF'R'
y' RU2R'UR2U'R2UR' [p] |
 |
FRU'R'
R2UR2U'RU2R'U2R [p]
(U')R'U2RU'RU'R2U2R' [s] |
 |
RU'R'U2RU2R' [p] |
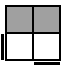 |
RU'R'UR2U'R2' [s]
RU2R'U2RUR' [p] |
 |
R'URUR' [s]
R'U'RUR'UR2U'R2 [p] |
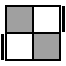 |
y' RU'R'U'R [s]
(U)RU'R'UR'U2RU2R [p] |
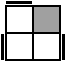 |
y' R'U'RUR'U'R [p] |
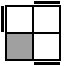 |
RUR'U'RUR' [p] |
 |
RU2R'U'R2U'R2' [s]
RU2RU2R2U'R2U'R2 [p] |
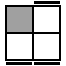 |
y' RUR2U'RUR2 [s]
x UR'U'RUR'U'R [p] |
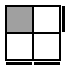 |
RU'R'URU'R' [p] |
 |
y' R'URU'R'UR [p] |
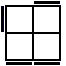 |
RU'R2'FRF'
(U)RU'RU2R'UR2 [s]
(U2)RU'R2U2RUR2U'R2U2R [p] |
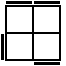 |
y' R'UR'U2RU'R2 [s]
R'U'RU'RU2R'UR'U'R2 [p] |
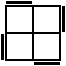 |
y' R'U2R'UR'U2R' [s]
R'U2RU2R'U2RU'RU'R2 [p] |
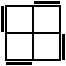 |
RU2RU'RU2R [s]
R2UR'UR'U2RU2R'U2R [p] |
Bar Subset
The following 7 cases are used when the two unoriented pieces of the bottom layer form a bar on the side.
Bottom →
Top ↓ |
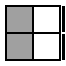 |
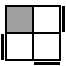 |
R'FR2F'U'R2
(U)R2U2R'UR'U2RUR2 [s]
RU'R2U'R2UR'U'R2UR' [p] |
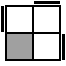 |
RUR'FRF'R2
(U)R2U2R'U'RU2R'U'R2 [s]
(U)R'U2RU'RUR2U'RUR' [p] |
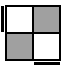 |
R'UR2U'R [s]
R'U2R'U2RU'R2U'R [p] |
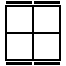 |
R'U'R2U'R2U'R' [s]
R'U2R2U'RU2R2U'R2 [p] |
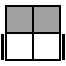 |
R2FR2FR2
(U')R2U'R2U2RU2R'U2R2 [p] |
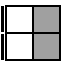 |
R2U'R2U2R' [p] |
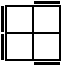 |
R'FRF'R'UR'
(U)R2U2R'U'R2U2R [p] |
No Bar Subset
These 7 algorithms are used when neither of the 2 unoriented pieces on the bottom layer are pointing to the side.
Bottom →
Top ↓ |
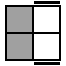 |
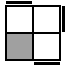 |
y' RU2RU2R'B
RUR'UR2U2R'U2R' [s]
R2U'R'UR2U'R2U'RU2R' [p] |
 |
y' B'RU2R'U2R'
(U2)RUR'U'RU2R'U2R [s]
(U)R'U2RU2R'U2RUR2UR' [p] |
 |
R2UR'U'FU'R'
R'UR2UR'U2RU2R [p] |
 |
RU2R'U2RU2R'U2R [s]
R'U2R2U'RU2R2U'R2 [p] |
 |
y FR2U'R2
R'U2R2U'R2 [p] |
 |
y' R2BR2B'R2
R'U2RU2RU2R'UR2 [p] |
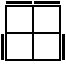 |
R'U'RU'RU'R2 [p] |
Asymetric Subset
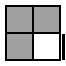
For these remaining 16 cases, you have 2 unoriented pieces on the bottom layer, and only one of them points to the side.
Bottom →
Top ↓ |
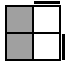 |
Bottom →
Top ↓ |
 |
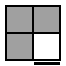 |
FRU2R'U'R
(U')R2URU'RUR2 [p] |
 |
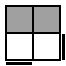
y R'URU2R'F'
R2U'R'UR'U'R2 [p] |
 |
x RUR'U'RUR'U' [p] |
 |
x URU'R'URU'R' [p] |
 |
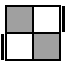
R2UR'U2R'U'R [p] |
 |
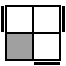
R'URU2RU'R2 [p] |
 |
RU'FRF'
R2U2RU2R'UR'U2R [s]
R'U'R2UR2U'R2UR'UR' [p] |
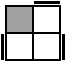 |
R'D'R'U'R
R2U2R'U2RU'RU2R' [s]
RUR2U'R2UR2U'RU'R [p] |
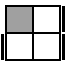 |
R2UR'FR2F'
R'UR'U2RU'RU'R'UR2 [p] |
 |
FR2F'RU'R2
RU'RUR2U'RUR2U'R [s]
(U')R2U2R'U2R2U'RU'RU'R [p] |
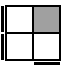 |
RUR'U2R [s]
(U')R'U2R'UR'UR2U'R2UR2 [p] |
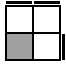 |
R'U2RU'R' [s]
RU2RU'RU'R2UR2U'R2 [p] |
 |
R'UR'UR' [p] |
 |
RU'RU'R [p] |
 |
R'U'R2U'R'U'R2 [p] |
 |
RURU2RUR [p] |
















































